-
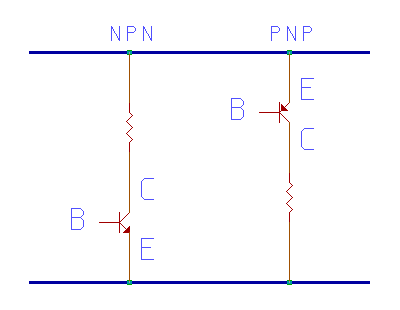
Transistors : NPN (left) and PNP (right) - Figure 6-1, above.
-
The transistor is a 3-terminal device which is essentially used for amplifying current. By some configuration, it can be used for amplifying voltages and many other applications.
-
The current between the base and the emitter is multiplied by an amplification factor to get the maximum current that could be allowed by the transistor to pass through its collector and emitter.
-
The amplification factor is inherent to the materials of the transistor. This amplification factor goes by many names, and for our purposes, we will call it "beta". If the "base-emitter" current is 10 milliamperes and the beta is 20, this specific transistor will be capable of delivering a maximum "collector-emitter" current of (10*20), or 200 milliamperes (mA).
 Figure 6-3 Figure 6-3
-
A transistor current amplifier.
 Figure 6-3 Figure 6-3
|
|
 Figure 6-3
Figure 6-3
 Figure 6-3
Figure 6-3